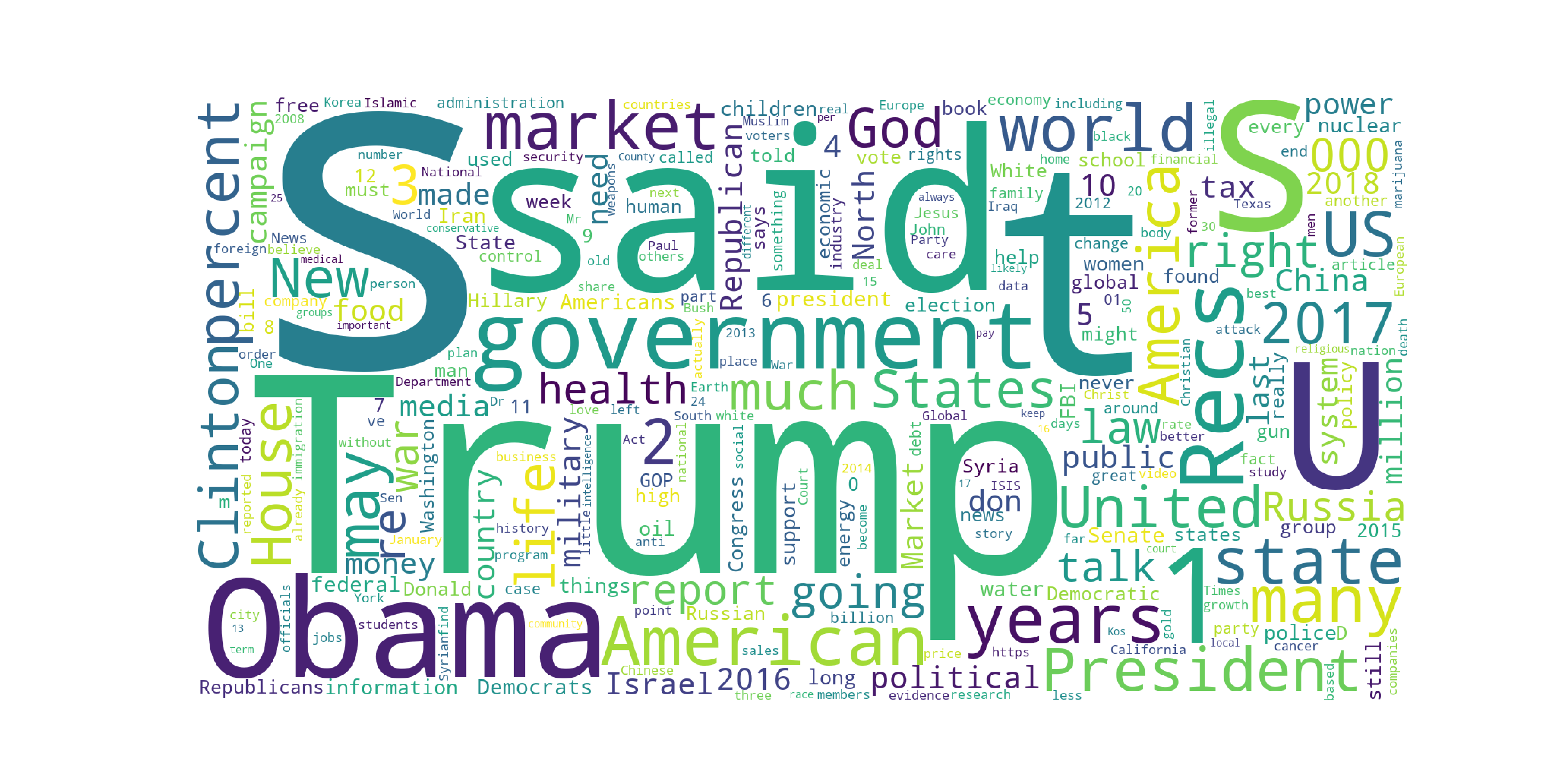
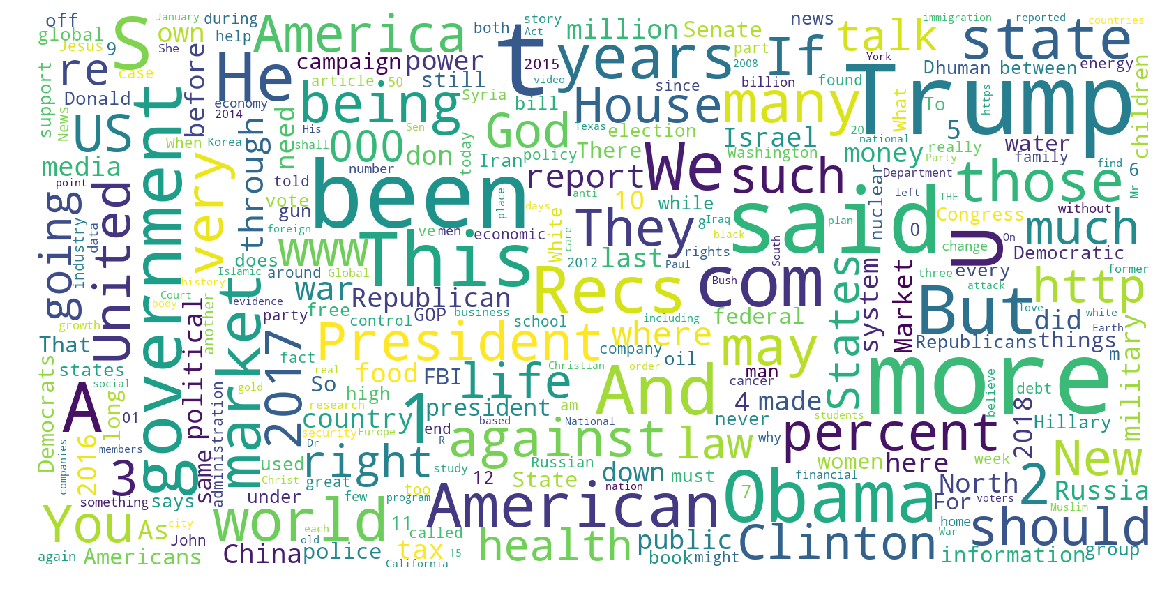
Discussion
Bias
The findings of this report are limited due to the bias of data collection being primarily United States. An interesting finding was the highly biased articles are very common in Russia. Bias is also very evenly distributed throughout the United States, showing it is a common otccurrence in news. Evenly distributed here actually is indicated by the east and west coast hosting a majority of the articles while the midwest is normally quite barren.
Conspiracy
Conspiracy articles were prevalent in the Netherlands while other categories were not. Although this is the case, most of the words found common in the sample set of articles were American focused, such as "Obama", "Trump", and "Clinton. Some other common trends found in Netherlands conspiracies were Islamic or Muslim related terminology.
Hate
Hate articles were only commonly hosted in the United States and were ironically primarily hosted in California. Political articles are well distributed in the United States with some articles hosted in the Netherlands.
Rumor
An interesting finding about articles classified as rumor, is that they are most commonly hosted in Seattle Washington, where I grew up! Some of the most common words included "Trump", "Clintom", "Obama", "Market", and "government" showing that the articles focused on rumores related to political topics.
Satire
Articles classified as satire are more common amongst other countries with articles being hosted not only in the United States but also the United Kingdom, France and Germany. The word cloud generation shows mostly French language stopwords which is a limitation of this dataset. During the generation, filtering of most common words were done with a list of english common words, which is why other language like "de" and "que" became the majority. Future work here would be to include other language stop words in order to only focus on meaninful words.
Unreliable
Unreliable articles were evenly distributed throughout the United States with the most common words being politicaly focused.
Junksci
This category was the only category that showed significant differences in most common words without any mention of presidential candidates. The most common terms here were "health", "foods" and "cancer" showing that the articles are health focused which also indicates a huge problem. If these articles are not only junk, but spreading incorrect information related to health, it could lead to readers making decisions that could harm them.
Future Work
Future work in high level data summary should generate word clouds or common terminology on the full dataset
in addition to other datasets to add diversity and mitigate the bias of collection being primarily from
articles hosted in the US. Another important research question is how many of these websites are hosted in one
country but are intended to be viewed by readers in another. An example in the dataset was a '.uk' website was
hosted in the United States but is clearly intended for readers in the UK. On this note as well, collecting
updates on these websites to see if their IP addresses change and to where, this could help determine if a
site is unreliable and changing IP addresses in order to reduce its chances of being reported or blocked.
Future work on a deeper level should be on developing machine learning algorithms to learn the distribution of
articles under each category and country. Part of this reasearch needs to take language into account as feature
extraction may differ and the distributions of the articles based on language may be easier to capture seperately
rather than including all languages for a class. Some models could use recurrent deep learning models to better
capture the context of words in the article. Decsision trees are another option as they would help understand
why a classification was made by looking at the tree splits. Finally, an adversarial autoencoder may be an
an interesting model to represent the data as not only could you classify data, but you could also generate
samples from the distributions it learns and either add that as new samples to a training set or use samples
for future research.